Ajax- 动态更新Web页面
导航: 上一页 | ASP | PHP | JSP | HTML | CSS | XHTML | aJAX | Ruby | JAVA | XML | Python | ColdFusion
如前所述,如果页面中只有一小部分需要修改,此时Ajax技术最适用。换句话说,以前实现一些用例时,为了更新页面中的一小部分总是需要使用完全页面刷新,这些用例就很适合采用Ajax技术
考虑一个有单个页面的用例,用户向这个页面输入的信息要增加到列表中。在这个例子中,你会看到列出某个组织中员工的Web页面。页面最上面有3个输入框,分别接受员工的姓名、职位和部门。点击Add(增加)按钮,将员工的姓名、职位和部门数据提交到服务器,在这里将这些员工信息增加到数据库中。
当使用传统的Web应用技术时,服务器以重新创建整个页面来做出响应,与前一个页面相比,惟一的差别只是新员工信息会增加到列表中。在这个例子中,我们要使用Ajax技术异步地将员工数据提交到服务器,并把该数据插入到数据库中。服务器发送一个状态码向浏览器做出响应,指示数据库操作是否成功。假设数据库成功插入,浏览器会使用JavaScript DOM操作用新员工信息动态更新页面内容。这个例子中还创建了Delete(删除)按钮,以便从数据库中删除员工信息。
代码清单4-13显示了HTML Web页面的源代码。这个页面有两部分:第一部分包括一些输入框,分别接受员工姓名、职位和部门的数据,以及启动数据库插入的Add按钮;第二部分列出数据库中的所有员工,每个记录有自己的Delete按钮,从而能从数据库删除这个记录的信息。
代码清单4-13 employeeList.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Employee List</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
var xmlHttp;
var name;
var title;
var department;
var deleteID;
var EMP_PREFIX = "emp-";
function createXMLHttpRequest() {
if (window.ActiveXObject) {
xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP");
}
else if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xmlHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
}
function addEmployee() {
name = document.getElementById("name").value;
title = document.getElementById("title").value;
department = document.getElementById("dept").value;
action = "add";
if(name == "" || title == "" || department == "") {
return;
}
var url = "EmployeeList?"
+ createAddQueryString(name, title, department, "add")
+ "&ts=" + new Date().getTime();
createXMLHttpRequest();
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = handleAddStateChange;
xmlHttp.open("GET", url, true);
xmlHttp.send(null);
}
function createAddQueryString(name, title, department, action) {
var queryString = "name=" + name
+ "&title=" + title
+ "&department=" + department
+ "&action=" + action;
return queryString;
}
function handleAddStateChange() {
if(xmlHttp.readyState == 4) {
if(xmlHttp.status == 200) {
updateEmployeeList();
clearInputBoxes();
}
else {
alert("Error while adding employee.");
}
}
}
function clearInputBoxes() {
document.getElementById("name").value = "";
document.getElementById("title").value = "";
document.getElementById("dept").value = "";
}
function deleteEmployee(id) {
deleteID = id;
var url = "EmployeeList?"
+ "action=delete"
+ "&id=" + id
+ "&ts=" + new Date().getTime();
createXMLHttpRequest();
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = handleDeleteStateChange;
xmlHttp.open("GET", url, true);
xmlHttp.send(null);
}
function updateEmployeeList() {
var responseXML = xmlHttp.responseXML;
var status = responseXML.getElementsByTagName("status")
.item(0).firstChild.nodeValue;
status = parseInt(status);
if(status != 1) {
return;
}
var row = document.createElement("tr");
var uniqueID = responseXML.getElementsByTagName("uniqueID")[0]
.firstChild.nodeValue;
row.setAttribute("id", EMP_PREFIX + uniqueID);
row.appendChild(createCellWithText(name));
row.appendChild(createCellWithText(title));
row.appendChild(createCellWithText(department));
var deleteButton = document.createElement("input");
deleteButton.setAttribute("type", "button");
deleteButton.setAttribute("value", "Delete");
deleteButton.onclick = function () { deleteEmployee(uniqueID); };
cell = document.createElement("td");
cell.appendChild(deleteButton);
row.appendChild(cell);
document.getElementById("employeeList").appendChild(row);
updateEmployeeListVisibility();
}
function createCellWithText(text) {
var cell = document.createElement("td");
cell.appendChild(document.createTextNode(text));
return cell;
}
function handleDeleteStateChange() {
if(xmlHttp.readyState == 4) {
if(xmlHttp.status == 200) {
deleteEmployeeFromList();
}
else {
alert("Error while deleting employee.");
}
}
}
function deleteEmployeeFromList() {
var status =
xmlHttp.responseXML.getElementsByTagName("status")
.item(0).firstChild.nodeValue;
status = parseInt(status);
if(status != 1) {
return;
}
var rowToDelete = document.getElementById(EMP_PREFIX + deleteID);
var employeeList = document.getElementById("employeeList");
employeeList.removeChild(rowToDelete);
updateEmployeeListVisibility();
}
function updateEmployeeListVisibility() {
var employeeList = document.getElementById("employeeList");
if(employeeList.childNodes.length > 0) {
document.getElementById("employeeListSpan").style.display = "";
}
else {
document.getElementById("employeeListSpan").style.display = "none";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
v<h1>Employee List</h1>
<form action="#">
<table width="80%" border="0">
<tr>
<td>Name: <input type="text" id="name"/></td>
<td>Title: <input type="text" id="title"/></td>
<td>Department: <input type="text" id="dept"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3" align="center">
<input type="button" value="Add" onclick="addEmployee();"/>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<span id="employeeListSpan" style="display:none;">
<h2>Employees:</h2>
<table border="1" width="80%">
<tbody id="employeeList"></tbody>
</table>
</span>
</body>
</html>
点击Add按钮启动数据库插入操作。基于Add按钮的onclick事件将调用addEmployee函数。addEmployee函数使用createAddQueryString来建立查询串,其中包括用户输入的员工姓名、职位和部门信息。创建XMLHttpRequest对象并设置onreadystatechange事件处理程序后,请求提交到服务器。
代码清单4-14列出了处理请求的Java servlet,当接收到请求时将调用servlet的doGet方法。这个方法获取查询串action参数的值,并把请求指向适当的方法。如果是增加信息,请求指向addEmployee方法。
代码清单4-14 EmployeeListServlet.java
package ajaxbook.chap4;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class EmployeeListServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void addEmployee(HttpServletRequest request
, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//Store the object in the database
String uniqueID = storeEmployee();
//Create the response XML
StringBuffer xml = new StringBuffer("<result><uniqueID>");
xml.append(uniqueID);
xml.append("</uniqueID>");
xml.append("</result>");
//Send the response back to the browser
sendResponse(response, xml.toString());
}
protected void deleteEmployee(HttpServletRequest request
, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String id = request.getParameter("id");
/* Assume that a call is made to delete the employee from the database */
//Create the response XML
StringBuffer xml = new StringBuffer("<result>");
xml.append("<status>1</status>");
xml.append("</result>");
//Send the response back to the browser
sendResponse(response, xml.toString());
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String action = request.getParameter("action");
if(action.equals("add")) {
addEmployee(request, response);
}
else if(action.equals("delete")) {
deleteEmployee(request, response);
}
}
private String storeEmployee() {
/* Assume that the employee is saved to a database and the
* database creates a unique ID. Return the unique ID to the
* calling method. In this case, make up a unique ID.
*/
String uniqueID = "";
Random randomizer = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
uniqueID += randomizer.nextInt(9);
}
return uniqueID;
}
private void sendResponse(HttpServletResponse response, String responseText)
throws IOException {
response.setContentType("text/xml");
response.getWriter().write(responseText);
}
}
addEmployee函数负责协调数据库插入和服务器响应。addEmployee方法委托store- Employee方法完成具体的数据库插入。在实际实现中,storeEmployee方法很可能调用数据库服务,由它处理数据库插入的具体细节。在这个简化的例子中,storeEmployee将模拟数据库插入,其方法是生成一个随机的惟一ID,模拟实际数据库插入可能返回的ID。生成的惟一ID再返回给addEmployee方法。
假设数据库插入成功,addEmployee方法则继续准备响应。响应是一个简单的XML串,它向浏览器返回一个状态码。XML通过串连接创建,然后写至响应的输出流。
浏览器通过调用handleAddStateChange方法来处理服务器的响应。只要XMLHttpReq-
uest对象发出信号指出其内部准备状态有变化,就会调用这个方法。一旦readystate属性指示服务器响应已经成功完成,就会调用updateEmployeeList函数,然后再调用clear-
InputBoxes函数。updateEmployeeList函数负责把成功插入的员工信息增加到页面上显示的员工列表中。clearInputBoxes函数是一个简单的工具方法,它会清空输入框,准备接收下一个员工的信息。
updateEmployeeList函数向表中增加行以列出员工的信息。首先使用document.cre-
ateElement方法来创建表行的一个实例。这一行的id属性设置为包括由数据库插入生成的惟一ID的值。id属性值惟一地标识了表行,这样点击Delete按钮时就能很容易地从表中删除这一行。
updateEmployeeList函数使用名为createCellWithText的工具函数来创建表单元格元素,其中包含指定的文本。createCellWithText函数分别为用户输入的姓名、职位和部门信息创建表单元格,再把各个单元格增加到先前创建的表行中。
最后要创建的是Delete按钮以及包含这个按钮的单元格。使用document.createElement方法创建通用的输入元素,其type和value属性分别设置为button和Delete,这样就能创建Delete按钮。再创建表单元格,用来放置Delete按钮,并把Delete按钮作为子元素增加到表单元格。然后把这个单元格增加到表行,接下来将这一行增加到员工列表中,现在行中已经包含了对应员工姓名、职位、部门和Delete按钮的单元格。
删除员工与增加员工的工作是一样的。Delete按钮的onclick事件处理程序调用delete-
Employee函数,将员工的惟一ID传递给这个函数。此时创建一个简单的查询串,指示想做的动作(删除)和要删除的员工记录的惟一ID。XMLHttpRequest对象的onreadystatechange属性设置为所需的事件处理程序后,提交请求。
EmployeeListServlet servlet使用deleteEmployee方法来处理员工删除用例。这个例子做了简化,在此假设还有另一个方法处理数据库删除的具体细节。如果成功地完成了数据库删除,deleteEmployee方法会准备XML串,返回给浏览器。与员工增加用例类似,这个用例向浏览器返回一个状态码。一旦创建XML串,则将XML串通过响应对象的输出流写回到浏览器。
浏览器通过handleDeleteStateChange函数处理服务器响应,如果响应成功,将转发到deleteEmployeeFromList方法。deleteEmployeeFromList函数从XML响应获取状态码,如果状态码指示删除不成功,这个函数将立即退出。假设成功地完成了删除操作,这个函数则会继续,使用document.getElementById方法获取表示所删除信息的表行,然后使用表体的removeChild方法从中删除这一行。
为什么不使用setattribute方法来设置DELETE按钮的事件处理程序?
你可能已经注意到,设置Delete按钮的事件处理程序时采用了何种方法。你可能认为,设置Delete按钮的onclick事件处理程序的代码应该如下所示:
deleteButton.setAttribute("onclick", "deleteEmployee('" + unique_id + "');");
确实,这个代码从理论上是对的,它遵循W3C标准,而且在大多数当前浏览器中都可行,只有IE例外。幸运的是,对于IE也有一个解决办法,它可以在Firefox、Opera、Safari和Konqueror中适用。
这种解决办法是使用点记法引用Delete按钮的onclick事件处理程序,然后使用调用deleteEmployee函数的匿名函数来设置事件处理程序。
图4-14显示了实际运行的动态更新例子。
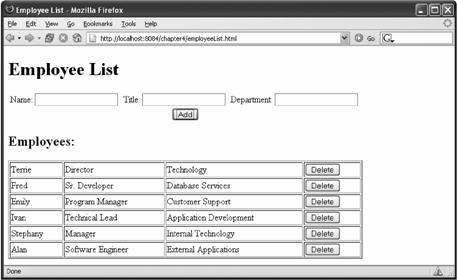 图4-14 每次点击Add按钮时每个姓名动态增加到列表中,而不必每次都刷新页面
图4-14 每次点击Add按钮时每个姓名动态增加到列表中,而不必每次都刷新页面
